Inhibition of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons Formation During Supercritical Water Gasification of Sewage Sludge by H2O2 Combined with Catalyst.
- DOI码:10.3390/w16223235
- 发表刊物:Water
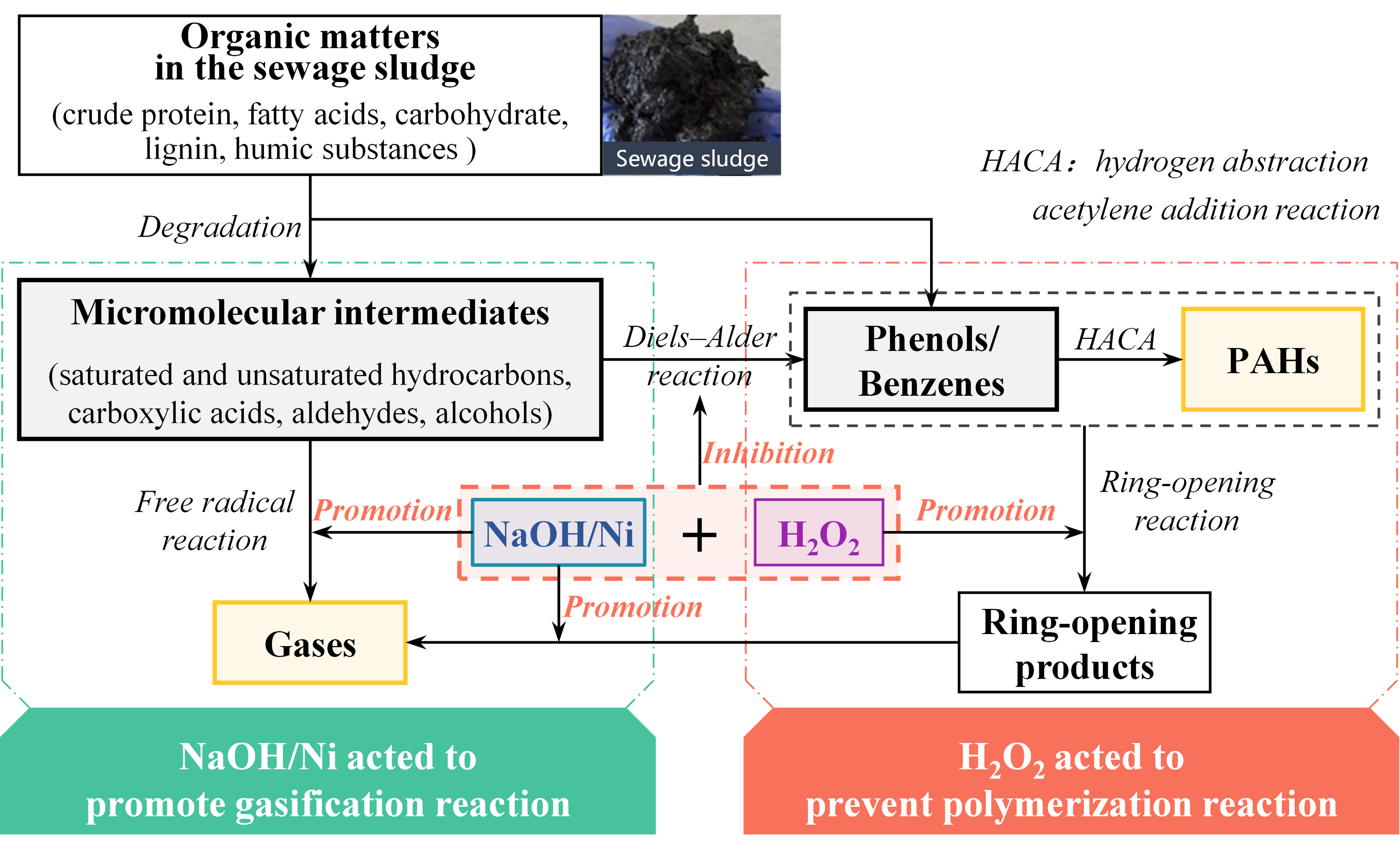
- 摘要:This work evaluated the alterations in the levels and types of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) within both liquid and solid products throughout the process of the catalytic supercritical water gasification of dewatered sewage sludge to examine the catalytic effect of various catalysts and the inhibit reaction pathways. The addition of Ni, NaOH, Na2CO3, H2O2, and KMnO4 reduced the concentrations of PAHs, with Ni and H2O2 showing the best performance. The concentrations of PAHs, especially higher-molecular-weight compounds in the residues, decreased sharply as the H2O2 amount increased. At a 10 wt% H2O2 addition, the levels of PAHs in the liquid and solid products were reduced by 91% and 88%, respectively. High-ring PAHs were not detected in the residues as the H2O2 amount increased to an 8 wt%. H2O2 addition evidently inhibits PAH formation by promoting the ring-opening reactions of initial aromatic compounds in raw sludge and inhibiting the polymerization of open-chain intermediate products. The addition of NaOH + H2O2 or Ni + H2O2 as combined catalysts significantly lowered PAH concentrations while increasing the H2 yield. The addition of 5 wt% Ni + H2O2 reduced PAH concentrations in the liquid and solid residues by 70% and 44%, respectively, while the H2 yield escalated from 0.13 mol/kg OM to 3.88 mol/kg OM. Possible mechanisms associated with the reaction pathways of these combined catalysts are proposed.
- 论文类型:期刊论文
- 卷号:22
- 期号:16
- 页面范围:3235
- 是否译文:否
- 发表时间:2024-11-11
- 收录刊物:SCI
- 发布期刊链接:https://doi.org/10.3390/w16223235
附件:
water-16-03235.pdf