Effect of CuSO4 on the behavior of nitrogen during supercritical water gasification of microalgal biomass
Release time:2024-08-09 Hits:
DOI number:10.1016/j.jece.2024.113737
Journal:Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering
Key Words:Microalgal biomass
Supercritical water gasification
CuSO4
Nitrogen transformation
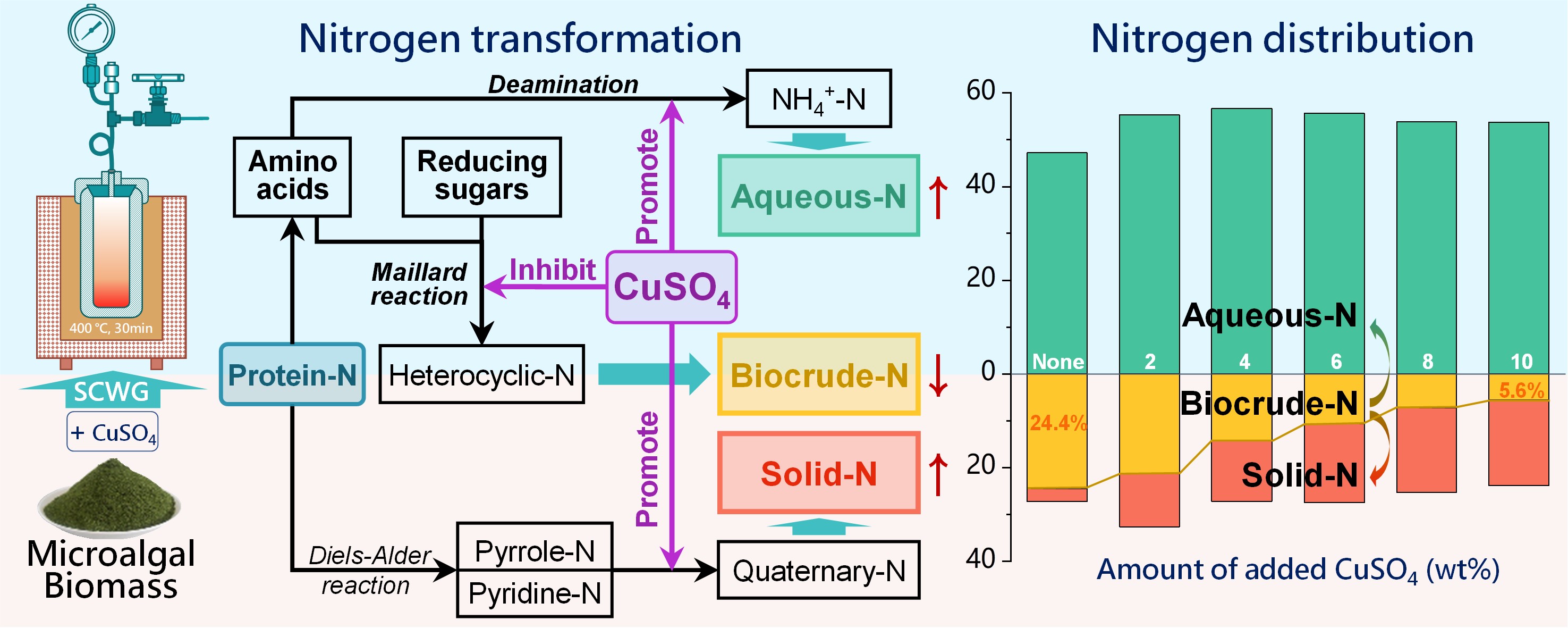
Abstract:This study investigated the effect of added CuSO4 on the behavior of nitrogen during the supercritical water gasification (SCWG) of microalgal biomass. The results showed that CuSO4 inhibited the entry of N into the biocrude product and promoted the transfer of N into the solid and aqueous products during SCWG. Upon increasing the amount of CuSO4, the biocrude-N content decreased continuously, while the solid-N and aqueous-N contents increased continuously. When 10 wt% CuSO4 was added, the proportion of biocrude-N reached 5.56 %, and the proportions of solid-N and aqueous-N were 18.28 % and 58.78 %, respectively. In an aqueous solution, CuSO4 dissociates into Cu2+, which possesses strong oxidative properties that facilitate the removal of amino groups (-NH2) from amino acids. Therefore, CuSO4 increased the NH4+-N content in the aqueous product by promoting amino acid deamidation. Due to competition between amino acid deamidation and the Maillard reaction, CuSO4 inhibited the Maillard reaction, which reduced the proportion of nitrogen-containing heterocycles in the biocrude product. It also slightly promoted the conversion of pyridine-N to quaternary-N, allowing N to exist in more stable forms in the solid product. CuSO4 also inhibited the generation of heavy biocrude. These findings provide a valuable reference for regulating nitrogen during the SCWG of nitrogenous biomass.
Indexed by:Journal paper
Volume:12
Issue:5
Page Number:113737
Translation or Not:no
Date of Publication:2024-08-05
Included Journals:SCI
Links to published journals:https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2213343724018670
